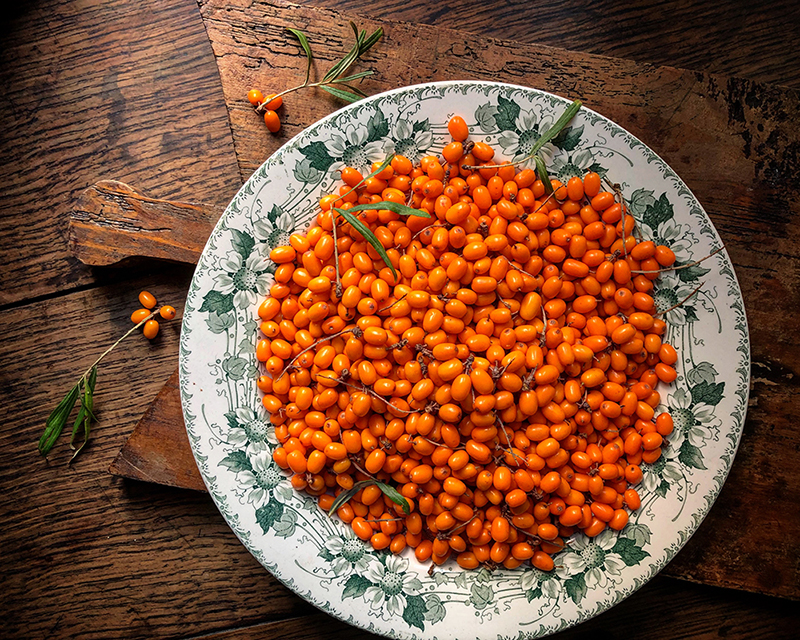
I first came into contact with these bright orange berries on one of my trips to Sweden last year. We visited a pick your own farm where the hedges of Sea buckthorn were plenty and laden with fruit. I wondered where these rough looking shrubs with their vicious thorns as dangerous as barb wire normally grow. Sea Buckthorn grows in coastal areas in Europe and Asia, in dunes and on moors. Their Flemish name translates to ‘Dune thorn’, other names are Sand Thorn and Siberian pineapple. Their roughness reflects the landscape in which they thrive. Brisk winds and cold, draught, desolate plains. Their root system is invasive, but improves marginal soil. In some areas the bushes have even been used for soil erosion control and land reclamation projects. It sort off feels like their thorns tell us to let them be, so that they can do good for the surrounding earth, the wildlife and to bring a highly healthy berry to the people that live around them. Birds can nest in the branches, benefiting from the piercing thorns as protection agains predators.
I first came into contact with these bright orange berries on one of my trips to Sweden last year. We visited a pick your own farm where the hedges of Sea buckthorn were plenty and laden with fruit. I wondered where these rough looking shrubs with their vicious thorns as dangerous as barb wire normally grow. Sea Buckthorn grows in coastal areas in Europe and Asia, in dunes and on moors. Their Flemish name translates to ‘Dune thorn’, other names are Sand Thorn and Siberian pineapple. Their roughness reflects the landscape in which they thrive. Brisk winds and cold, draught, desolate plains. Their root system is invasive, but improves marginal soil. In some areas the bushes have even been used for soil erosion control and land reclamation projects. It sort off feels like their thorns tell us to let them be, so that they can do good for the surrounding earth, the wildlife and to bring a highly healthy berry to the people that live around them. Birds can nest in the branches, benefiting from the piercing thorns as protection agains predators.
The oval berries are tart, bitter and have little sweetness to them. They have been used for medicinal purposes for centuries, they are full of anti-oxidants, beta-carotene, vitamine C, A and E and they battle inflammation. A concentrated puree from the berries can be used to relief sunburn and some say it could be good for some skin conditions. You could call them a super food, but lets forget about that horrible hipster term shall we? The young leaves can be used for tea because of their amino-acids, fatty acids, minerals and ability to boosting the immune system. An oil is made from the berries and seeds and used for all kinds of ails. In a nutshell, the berries are good for you and the shrub is a good one to have around.
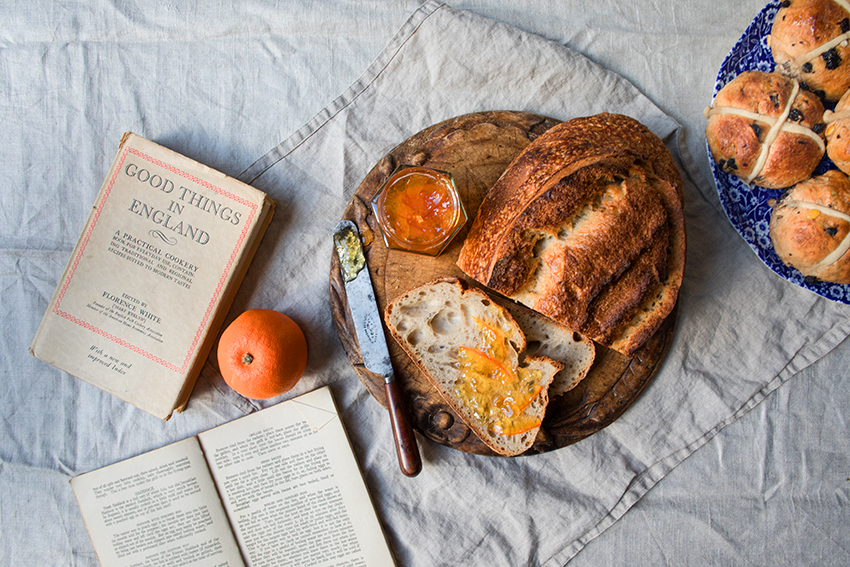
I enjoy the flavour, the mild tartness, their lack of sweetness. I bought a jar of Sea Buckthorn jam on my last trip to Sweden when I visited an apple orchard by the Baltic Sea. Of course because of their location they must have had a lot of Sea Buckthorn bushes around and in their shop they sold a jam called “Marmalat” which was more compote textured than jammy because they added a small amount of apple to the Sea Buckthorn. The jam was spread on toast and the jar empty much too soon so I started to look forward to the new Sea Buckthorn season and searched for a farm that grows the trees.
On an evening in late august my husband and I set out to visit a man with a passion for peculiar and otherwise difficult to find fruit bushes. Together we spent nearly half an hour harvesting just 500 grams of berries. The cruel thorns make harvesting very troublesome and the tree doesn’t like to let go of its berries very easily. The best method to harvest these berries and to prevent cuts in your hands from the thorns is to prune the bushes – that need a lot of pruning anyway – and freeze the branches whole. When frozen the berries are suddenly incredibly easy to pick and most just fall from the branches.
I wanted to make the jam and at the same time make as much of the fruit as I could. The jam was made by boiling the fruit, then straining the pulp. The pulp just keeps on giving, to the pulp of 500 g berries I added 1 liter of boiling water and left it to brew for half an hour. The juice that is left can be consumed as tea or juice and it is also makes a very good aperitif mixed with sparkling wine. My favourite thing to do with the juice however is to make a sorbet out of it. I’m not an ice cream lover because I’m not too fond of its sweetness but since these berries aren’t really sweet it makes for a perfect sorbet for me. Just freeze the juice in a shallow container and stir every 30 minutes until ready – or use a machine if you have one. Come to think of it, a slushy would work great too!…